In today’s digital landscape, the battle between Digital Marketing and Cybersecurity is intensifying.
As businesses rely more on online platforms to connect with their audiences, the risks of cyber threats and data breaches are ever-present.
On one side, digital marketers strategize and execute campaigns to capture attention and drive sales, while on the other, cybersecurity experts work tirelessly to protect valuable data and secure online transactions.
Both forces are crucial in their own ways, but how do they coexist and navigate this evolving landscape?
Let’s explore the contrasting worlds of Digital Marketing and Cybersecurity, their challenges, and the importance of finding a harmonious balance.

Digital Marketing vs. Cybersecurity: Digital Marketing
Definition
Digital marketing refers to the practice of promoting products or services using digital channels such as search engines, websites, social media, email, and mobile apps. It involves various activities, including creating and sharing content, engaging with customers, and analyzing data to optimize marketing efforts.
Importance
Digital marketing has become increasingly important in today’s technology-driven world. With more people using the internet and mobile devices, companies need to establish a strong online presence to reach their target audience effectively. It allows businesses to connect with customers on a global scale, increase brand awareness, drive website traffic, generate leads, and ultimately, drive sales.
Strategies
There are several digital marketing strategies that businesses can employ to achieve their marketing goals. These include search engine optimization (SEO), content marketing, social media marketing, email marketing, influencer marketing, and paid advertising. Each strategy has its unique advantages and can be combined to create a comprehensive marketing approach.
Techniques
Within each digital marketing strategy, there are various techniques that businesses can use to maximize their marketing impact. For example, in SEO, techniques such as keyword research, on-page optimization, link building, and technical SEO can help improve a website’s visibility in search engine results. In content marketing, techniques like creating engaging blog posts, videos, and infographics can attract and retain customers.
Targeting
One of the key advantages of digital marketing is the ability to target specific audiences. Through data analysis and segmentation, businesses can personalize their marketing messages and deliver them to the right people at the right time. Targeting can be based on demographics, interests, behaviors, or even previous interactions with the brand. This precision targeting increases the chances of converting prospects into customers.
Metrics
To measure the success of digital marketing efforts, businesses rely on various metrics. These include website traffic, conversion rates, click-through rates, engagement rates, cost per acquisition, return on investment, and customer lifetime value. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify what is working well and what needs improvement, allowing them to refine their digital marketing strategies effectively.
Tools
There are numerous digital marketing tools available to help businesses implement and manage their digital marketing campaigns. These tools include website analytics platforms (such as Google Analytics), email marketing tools (like Mailchimp), social media management tools (such as Hootsuite), content management systems (like WordPress), and customer relationship management systems (such as HubSpot). These tools provide businesses with valuable insights, automation, and integration capabilities to enhance their digital marketing efforts.
Trends
Digital marketing is a rapidly evolving field, and staying on top of the latest trends is crucial for success. Some of the current trends in digital marketing include the rise of video marketing, the importance of user-generated content, the growing influence of social media influencers, the increasing use of artificial intelligence and chatbots, and the shift towards personalized marketing experiences. By embracing these trends, businesses can stay competitive and effectively engage with their target audience.
Challenges
While digital marketing offers numerous opportunities, it also presents challenges that businesses must overcome. One major challenge is the increasing competition and cluttered digital landscape. With so many brands vying for consumers’ attention, capturing and retaining their interest can be difficult. Additionally, digital marketing requires continuous learning and adaptation as strategies and technologies evolve. It can be challenging to keep up with the ever-changing digital marketing landscape.
Benefits
Despite the challenges, digital marketing provides various benefits for businesses. It offers a cost-effective way to reach a wider audience compared to traditional marketing methods. It allows for real-time data analysis, enabling businesses to measure the effectiveness of their marketing efforts and make data-driven decisions. Digital marketing also provides unparalleled opportunities for customer engagement, fostering relationships and building brand loyalty. Ultimately, it helps businesses stay relevant, attract new customers, and grow their revenue.
Digital Marketing vs. Cybersecurity: Cybersecurity
Definition
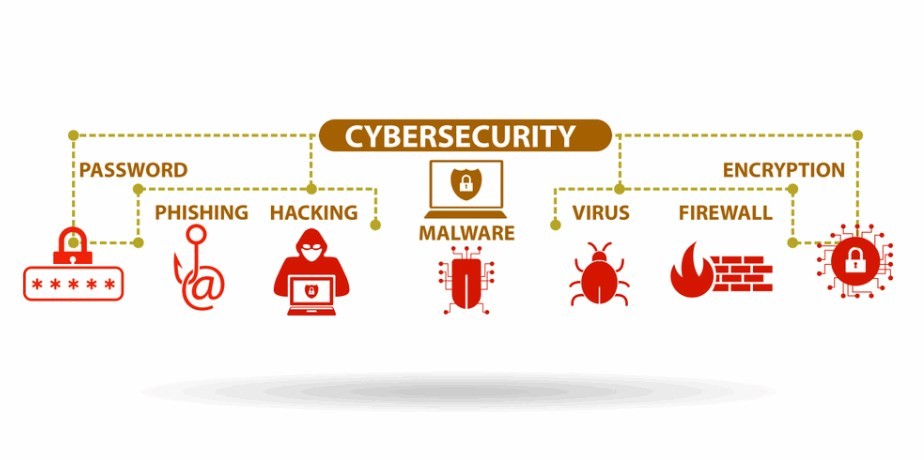
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, damage, or attacks. It involves implementing a range of technologies, processes, and strategies to safeguard digital assets and ensure the privacy, integrity, and availability of information.
Importance
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is of paramount importance. With the increasing reliance on technology and the vast amount of sensitive data stored electronically, the risk of cyber threats is higher than ever. A cybersecurity breach can have severe consequences, including financial loss, damage to a company’s reputation, legal repercussions, and compromised customer trust. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect sensitive information and maintain business continuity.
Threats
Cybersecurity faces a wide range of threats from various sources. These threats include cybercriminals, hacktivists, state-sponsored hackers, insiders, and even unintentional human errors. Cybercriminals use sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks for malicious purposes. Common cybersecurity threats include hacking, phishing, malware, ransomware, social engineering, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Types of Attacks
Cyber Attacks can be categorized into different types based on their objectives and techniques. Some of the most common types of cyber attacks include:
- Phishing: This attack involves sending fraudulent emails or messages to deceive individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card details.
- Malware: Malware refers to malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems or networks. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack: A DoS attack aims to make a computer system or network unavailable to users by overwhelming it with excessive traffic or resource requests.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack: In a MitM attack, an attacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop, steal information, or impersonate one of the parties.
Preventive Measures
To mitigate the risk of cyber attacks, organizations must implement preventive measures. These measures include:
- Strong Password Policies: Organizations should enforce password complexity requirements and recommend regular password changes to prevent unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens.
- Regular Software Updates and Patches: Keeping computer systems and software up to date with the latest security patches helps address known vulnerabilities and reduces the risk of exploitation.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as identifying phishing emails and avoiding suspicious websites, helps strengthen the organization’s defense against cyber threats.
Detection and Response
In addition to preventive measures, organizations must have robust detection and response capabilities to swiftly identify and mitigate cyber threats. This includes deploying intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) tools, and conducting regular security assessments and penetration testing. When a security incident occurs, an effective response plan ensures that the organization can contain the attack, investigate the incident, and restore normal operations as quickly as possible.
Technologies
Numerous technologies play a crucial role in cybersecurity. These include encryption algorithms, firewalls, antivirus software, intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), virtual private networks (VPNs), and secure socket layer (SSL) certificates. These technologies help protect data, authenticate users, monitor network traffic, and secure communications.
Compliance
With the growing emphasis on data privacy and protection, organizations must comply with industry-specific regulations and standards. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on how organizations handle personal data. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure the security and privacy of customer data and mitigates the risk of legal and financial consequences.
Skills and Roles
Cybersecurity requires a range of specialized skills and roles within organizations. These include:
- Security Analysts: Security analysts are responsible for monitoring and analyzing security incidents, investigating vulnerabilities, and recommending security improvements.
- Ethical Hackers: Ethical hackers, also known as penetration testers, identify vulnerabilities in computer systems and networks by attempting to exploit them. Their findings help organizations strengthen their security defenses.
- Security Engineers: Security engineers design and implement security infrastructure, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols, to protect computer systems and networks.
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO): The CISO oversees an organization’s cybersecurity strategy and ensures the implementation of effective security measures. They play a critical role in managing cyber risks and aligning security initiatives with business goals.
Future of Cybersecurity
As technology continues to advance, the future of cybersecurity holds both challenges and opportunities. With the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT), securing interconnected devices and data will become increasingly important. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can also be utilized to enhance threat analysis and detection capabilities. However, as cyber threats become more sophisticated, organizations must remain vigilant and continuously adapt their cybersecurity strategies to safeguard against emerging threats.




